Competency-Based Medical Education
What is Competency-based Medical Education?
Competency-based medical education (CBME) is an outcome-based approach to the design, implementation, assessment, and evaluation of medical education programs, using an organizing framework of competencies.
What is Competence by Design?
Competence by design (CBD) is the Royal College of Physicians of Surgeons of Canada’s initiative to transition the current time-based medical education model to a hybrid form of CBME. CBD does not shorten or adjust time spent in training; instead, it uses time as a resource for acquiring competencies.
Why change the current approach?
The rationale for transforming our current residency program to CBD can be summarized in four key principles of competency-based medical education:
- Focuses on outcomes.
- Emphasizes the abilities of the learner (not just his or her knowledge).
- De-emphasizes time as primary outcome metric of training.
- Promotes greater learner centeredness.
The goal is to enhance patient care by improving learning and assessment.
When do we expect our residency programs to transition to CBD?
All disciplines have been grouped into a cohort of CBD implementation by the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada. For the Internal Medicine core residency training program at Western University, all residents entering the program as of July 2019 will be trained under a CBD model. A soft launch occured July 2018. Implementation of CBD for Subspecialty programs depend upon the cohort in which that Subspecialty has been included.
What changes do we expect?
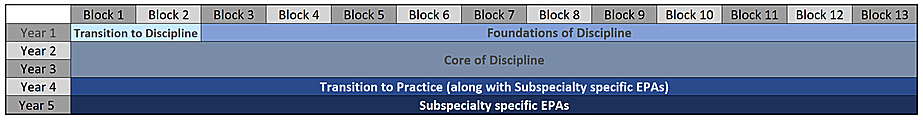
The Royal College has introduced the CBD Competence Continuum. The residency training program is divided into four developmental stages.
There are stage-specific outcomes that the trainees need to demonstrate competencies in prior to moving onto the next stage. The stages in residency training:
- Transition to discipline: This stage emphasizes orientation and assessment of new trainees.
- Foundations of discipline: This stage covers broad-based competencies.
- Core of discipline: This stage covers more advanced and discipline-specific competencies.
- Transition to practice: For Internal Medicine trainees, this stage will be part of their subspecialty training.
The stages of training are demonstrated below as applicable to our internal medicine training program.
How do trainees move onto the next stage in training?
There are Entrustable Professional Activities (EPAs) linked to each stage of the competence continuum. An EPA is a key task of a discipline that an individual can be trusted to perform without direct supervision in a given health care context, once sufficient competence has been demonstrated. Trainees will need to demonstrate competency in all the EPAs outlined in their stage of training in order to move onto the next stage.
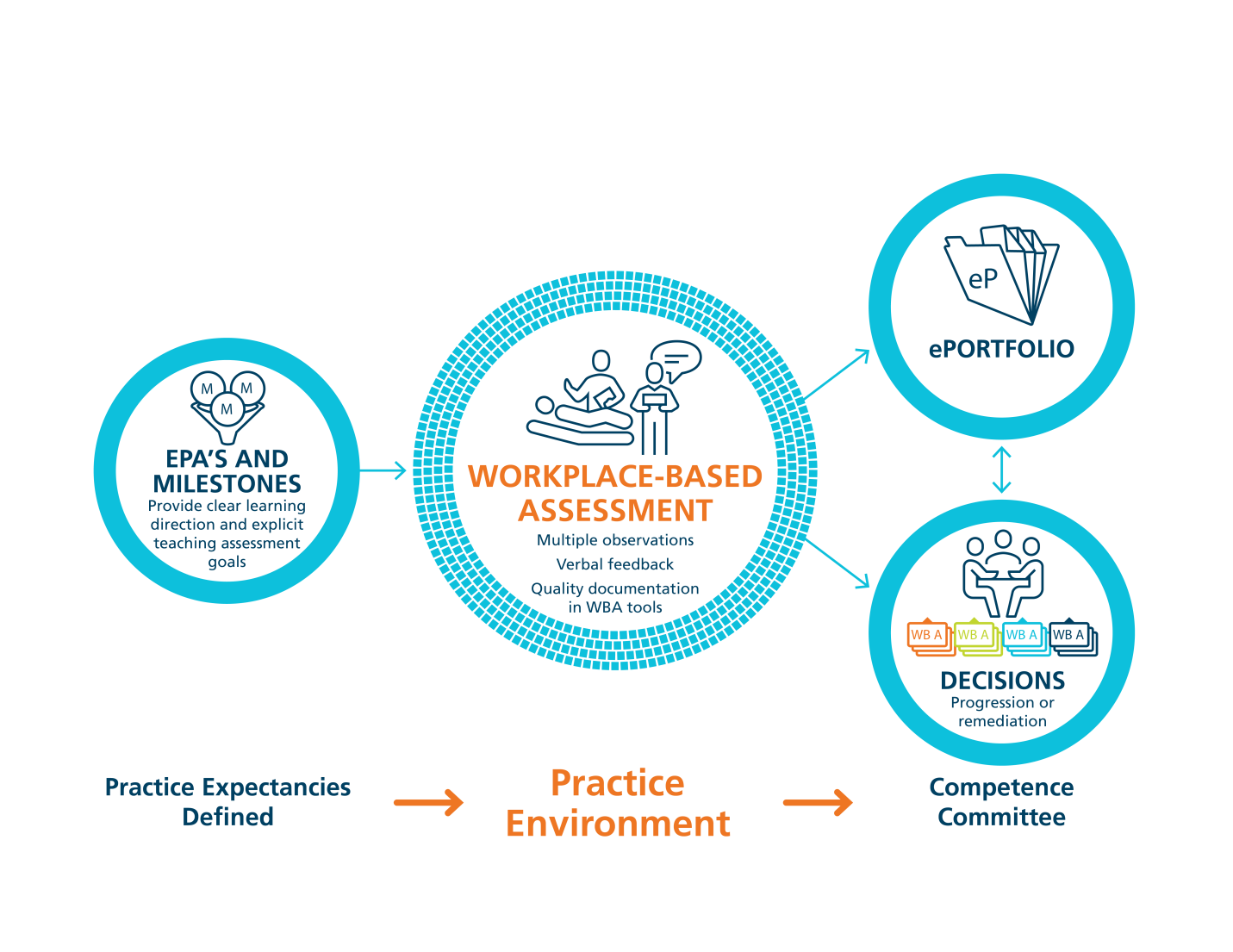
The competence committee will conduct robust and transparent resident performance reviews at least twice a year for each trainee over the course of their training. This will ensure each resident has demonstrated achievement of all EPAs within each stage of training.








