Undergraduate Selectives
The Division of Infectious Diseases is pleased to offer 2-week and 4-week selectives to 3rd and 4th year medical students at the Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry, and to visiting medical students from other Canadian and International Centres who meet eligibility requirements. The objective of this rotation is to introduce students to the vast array of infectious diseases cases typically encountered in a tertiary care teaching hospital. The educational focus of the rotation will be on the acquisition of the knowledge and skills required for the optimal assessment and management of common commonly encountered infectious diseases syndromes or their non-infectious disease mimics.
Selective students will be assigned to the Infectious Diseases consultation service at either University Hospital or Victoria Hospital. Opportunities also exist for students to spend time in one or two outpatient clinics during the rotation.
Our faculty members provide comprehensive clinical consultative services to a wide variety of adult patient populations at London's academic hospitals. These services are organized as separate programs at each hospital site, and are delivered by a team comprised of an Infectious Diseases consultant, Infectious Diseases subspecialty resident(s), internal medicine resident(s), family medicine residents, medical students, and pharmacists.
By the end of the selective rotation, the student will:
- Develop their history taking, physical examination, and clinical reasoning skills during their assessment of patients with a suspected infectious disease.
- Become familiar with the microbiology and clinical management of common infectious diseases syndromes, including
- HIV and related opportunistic infections, including a basic understanding of therapeutic principles
- Cellulitis/Skin and Skin Structure Infections
- Osteomyelitis/Septic arthritis
- Urinary tract infections
- Intraabdominal/Gastrointestinal infections
- Gynaecologic infections
- Respiratory tract infections
- Head and neck infections
- Fever of Unknown Origin
- Infections caused by antimicrobial-resistant organisms (AROs).
- Cardiovascular Infections
- Central Nervous System Infections
-
Understand the mechanism(s) of action and appropriate utilization of commonly prescribed antimicrobial agents in the inpatient setting.
- Communicate/collaborate effectively with team members, other healthcare providers, and patients.
A typical rotation schedule for a 4-week selective is shown below:
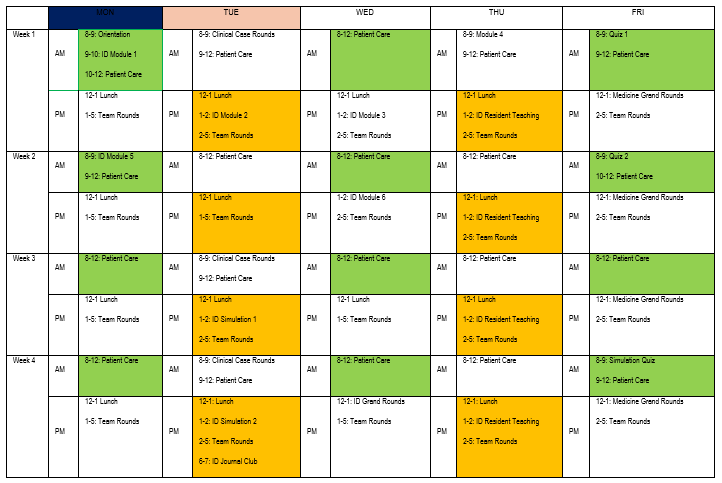
During each week of the selective, the student will complete several ID modules and three practice quizzes, as follows:
- ID Module 1 (Week 1): Textbook chapters
- ID Module 2 (Week 1): Review article
- ID Module 3 (Week 1): Textbook chapters
- Quiz 1 (Week 1)
- ID Module 4 (Week 2): Review article
- ID Module 5 (Week 2): Textbook chapters
- ID Module 6 (Week 2): Review article
- Quiz 2 (Week 2)
For students completing a 4-week selective, two simulation sessions will be also offered, along with a simulation quiz (for learning purposes only).
The Infectious Diseases provides clinical consultative services to the Intensive care unit, emergency, and various medical and surgical services.
Students interested in outpatient learning experiences may spend one or two half-days in one of our outpatient clinics at St. Joseph's Hospital, University Hospital, and Victoria Hospital.
There are no evening on-call duties for selective medical students on the Infectious Diseases Rotation. Selective students may be scheduled for a maximum of one weekend of home call.
Information on how to apply for an undergraduate selective rotation can be found on the Schulich School of Medicine's Undergraduate Medical Education webpage.








